FAQ - Frequently Asked
Questions
Electronic signatures and seals validation FAQ
A page with a collection of the most common questions and answers about our service verifysignature.eu and the subject of security services associated with an electronic signature under the eIDAS Regulation. Check the questions in the following tabs to get answers and find additional information.
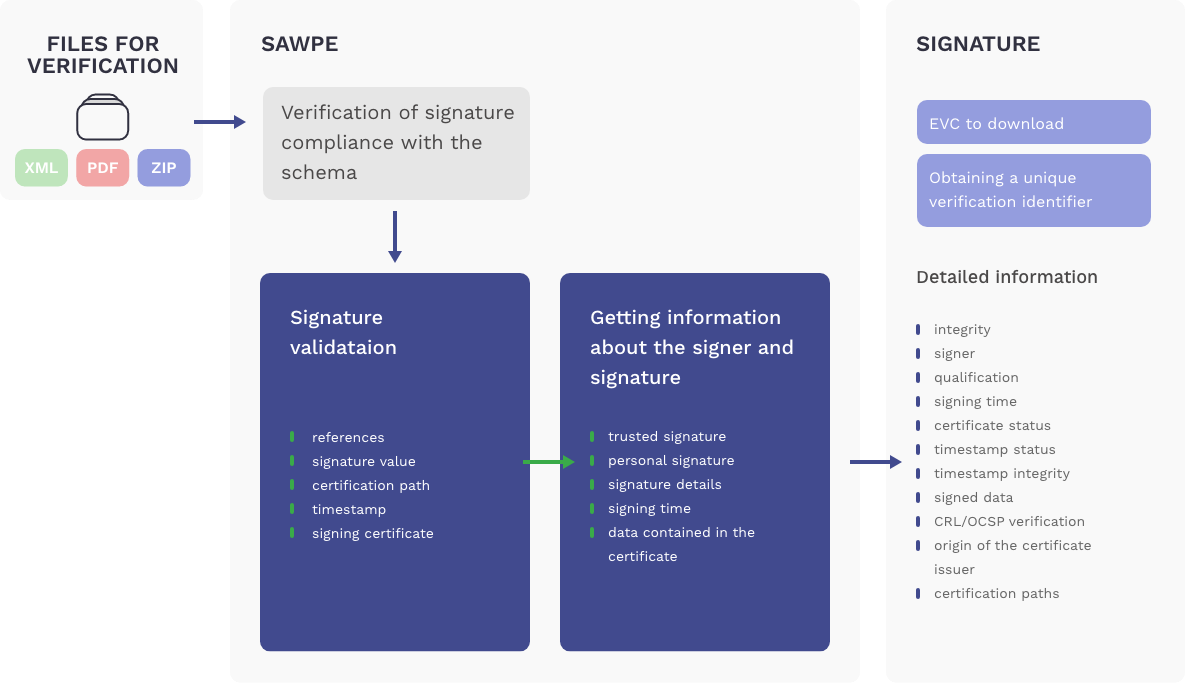
How to verify the signature in XAdES format?
In the case of signatures saved in a separate file with the name most often corresponding to the name of the signed file with the .xades extension, both files should be submitted to the verification process at the same time.
Otherwise, the system will inform you about the lack of file verification or lack of integrity.
Can I verify a packaged of packed files in RAR or ZIP format?
Yes, the verifier is able to automatically unpack the RAR and ZIP archive and verify its contents.
Which type of electronic signature should I use for a specific format of electronic signatures?
The eIDAS regulation identifies four main signature formats:
- XAdES, for XML documents and as an external signature for any files,
- PAdES, only for PDF documents,
- CAdES, a binary form, occurs in internal and external form,
- ASiC, this is a package/container containing many signed documents.
What does the status of unsupported signature format mean?
The verifier supports signature formats such as (XAdES, CAdES, PAdES, ASiC, PKCS7) at various validation levels, which are available on the main page of the application. Formats and forms not indicated on the website are not supported. In addition, such a message may appear in the case of an unsupported signature algorithm, document transforms even though the signature was saved in a supported format.
Is the SHA-2 algorithm required?
From July 1, 2018 in Poland (in accordance with the Act on trust and electronic identification services), the SHA-1 hash function should not be used to place electronic signatures. Instead, use the SHA-2 family functions. However, such a signature cannot be automatically considered invalid because it is currently not recommended in the standards, but is not deemed to be withdrawn. During verification, the system returns information about the hash function algorithm used, which should be currently considered when analyzing the verification result in a specific legal act.
What does the status mean: Certificate is not valid?
Status means that the certificate has expired. In the verification details you can find the expiry dates of the certificate. This information is important because at the time of verification of the electronic signature for which the signer’s certificate is no longer valid, there is no evidence that the document was signed during its validity period, and therefore at a time when it could be considered as valid. To this end, it is worth using signature time stamping.
What does the information mean: Incorrect certification path?
Status means a problem with finding the signing certification path on the CRL, TSL, OCSP lists side, whose task is to confirm the issuer of the certificate, its validity and details of the person to which the certificate was issued.
W jaki sposób najlepiej podpisać dokument w formacie PDF?
PAdES format is dedicated to PDF documents and using it does not cause problems with its verification, because verification software primarily verifies signatures fully compliant with EIDAS. In addition – standard software for reading PDF files also automatically presents the result of verification of just such a signature, and this signature is permanently associated with the signed document and there is no way (as opposed to an external signature) to “lose or forget it” when forwarding the document to the other legal act party.
Does an electronic power of attorney lose its validity upon the expiry of the power of attorney's certificate?
How to verify a foreign electronic signature?
Signatures that are supported by our verification system can be found on the European list of trusted service providers (TSL) located at https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/tl-browser. The TSL list includes certification service providers from EU and EEA countries (in accordance with eIDAS).
What does the lack of integrity mean?
The verified file has probably been modified after it was signed. An example of a loss of integrity may be, for example, giving a password to the file to be signed after it is signed. Integrity is the basic feature of an electronic signature which guarantees that the signed data has not been modified after it has been signed.
What does status mean: Signature verification is not possible?
The verification result informs for .xades files that the system was unable to find the signed files. If XADES files are external type signature files, in order for them to be verified, all files should be submitted to the verifier at the same time.
Is the signature verification service available at verifysignature.eu is a certified service?
The service on the website verifysignature.eu is provided by Madkom SA on the basis of an entry in the register of non-qualified NCCERT trust services in the field of Certificate status verification. Our certification may be used as evidence and has legal force resulting from the provision of a non-qualified electronic signature and electronic seal verification service.
A verification report is generated on the page. Can I also use this site and send documents, some of which are trade secrets of the Contractors?
Pursuant to the Policy of providing electronic signature verification service online, the system does not store any transferred files for verification. They are automatically deleted immediately after the verification process. Only the full signature verification result is saved in the system.
What is a document revision for PDF files?
Does the orange verification result for one of the signatures suggest an error? Should all signatures be green?
The orange color of the verification result always requires reviewing and analyzing the details of the verification and making a decision based on these data by the system user.
Is the service is able to confirm compliance with UPO issued by the authorities of the original documents which UPO were issued (shortcut document compliance with the abbreviation given in UPO)?
The application generally verifies the electronic signatures themselves, but the important step in verifying the signature is to check the document’s integrity by verifying the checksum. UPO structure generated, among others the ePUAP system includes such a mechanism by which, for the correct verification of UPO.xml, it is also required to verify the document to which it relates. A positive result of the UPO.xml verification confirms belonging to this UPO.
On what basis does the application determine the eligibility of an electronic signature if it is unable to confirm the certification path? Can you indicate a document with the minimum technical requirements that the certificate must meet in order to be considered qualified and acceptable?
A qualified certificate in accordance with eIDAS must contain information that can be automatically processed about the fact that it is a qualified certificate. In addition, the certificate or service registered on the TSL list requires the simultaneous conclusion of information about placing the associated private key on the so-called qualified device, e.g. QSCD. Based on this information, the application determines whether an advanced electronic signature can be considered qualified.
On what date is the qualified electronic signature made?
There can be many times associated with an electronic signature. First of all – at the time of submitting the electronic signature, the signing application retrieves the local time from the computer or device of the signer and places it in such a part of the signature that these data are signed. This is called the declared time of signing, so the signer has somehow signed this time. Other times are associated with the so-called timestamps. So, trusted and associated with the data to which the time stamp applies, time information from an external source. Of course, the use of a qualified tag gives the greatest confidence in the time contained in the tag. However, it should be taken into account that the time stamp can be added to the signature at any time after signing. Additionally, any person can do it – including the person verifying the electronic signature. With such a construction, it should be remembered that the time stamp only says about the existence of the signature at the time contained in the time stamp, and not about when exactly the document was signed. Adding a time stamp to the signature after the period of validity of the certificate does not guarantee us to sign the validity period. The addition of a time stamp during the period of validity of the signing certificate results in a kind of “extension” of the signature’s validity until the expiry of the time stamp’s certificate (provided that its validity ends later than the end of the signature’s certificate).
Don't see the answer to your question?
 FR
FR  DE
DE